신장 손상
임상양상
복부/옆구리 둔상 또는 관통상
flank ecchymosis, rib fracture
gross / microscopic hematuria
진단 및 손상 정도 평가 : 조영증강 CT
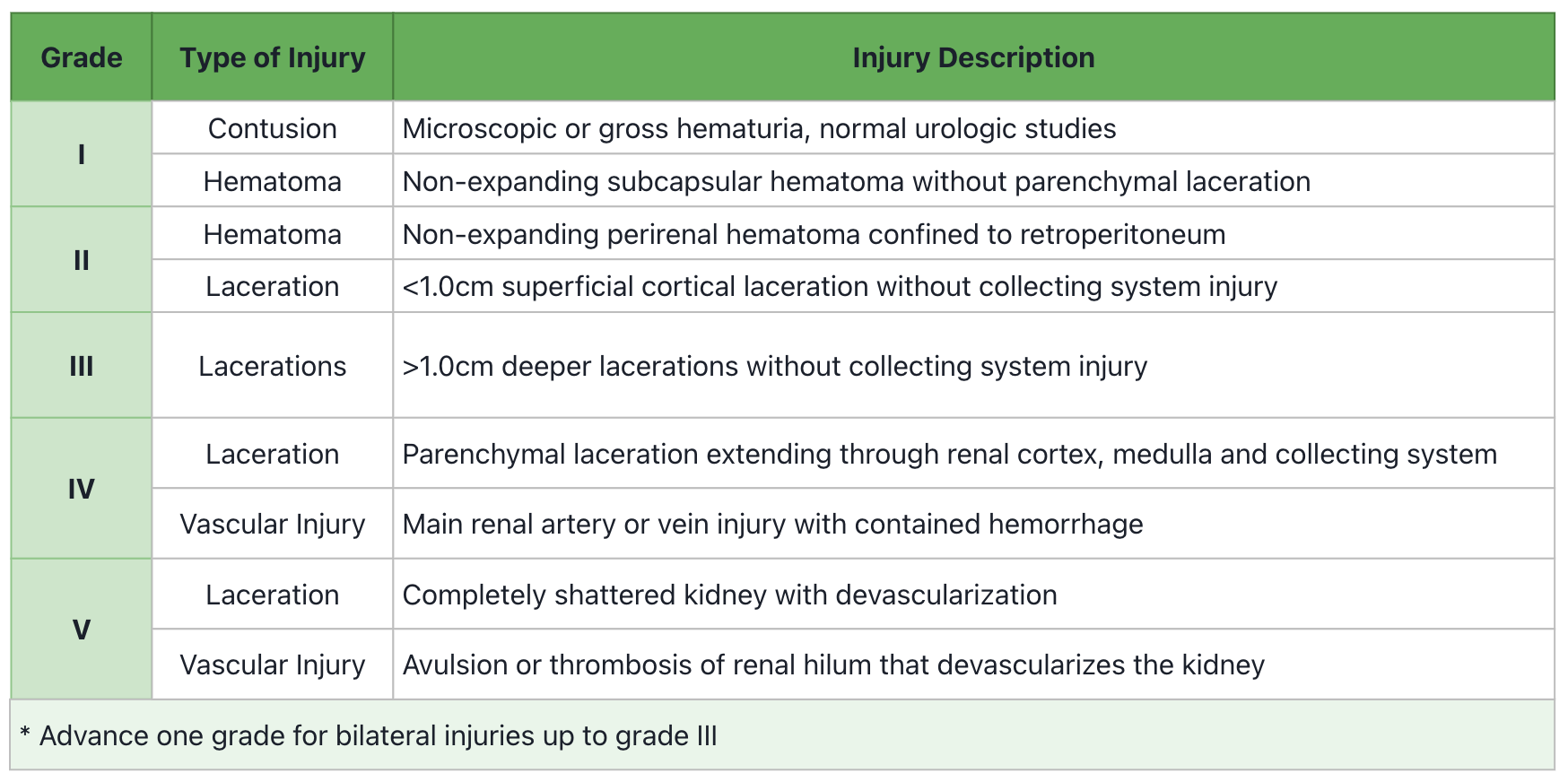
AAST Renal Injury scale
![Classification of renal trauma using the American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST) renal injury scale. Arterial and portal venous phase imaging is recommended for evaluation. Clinical or imaging findings suggesting collecting system injury should be followed by a delayed excretory phase to detect urine extravasation. The imaging classification criteria are as follows: grade 1 (A): subcapsular haematoma or contusion, without laceration; grade 2 (B–C): superficial laceration ≤ 1 cm depth not involving the collecting system with no evidence of urine extravasation (B) or perirenal haematoma confined within the perirenal fascia (C); grade 3 (D): laceration > 1 cm not involving the collecting system, vascular injury or active bleeding confined within the perirenal fascia; grade 4 (E): laceration involving the collecting system with urinary extravasation, laceration of the renal pelvis, vascular injury to segmental renal artery or vein, segmental infarctions without associated active bleeding or active bleeding extending beyond the perirenal fascia, grade 5 (F–G): shattered kidney (F), avulsion of renal hilum or laceration of the main renal artery or vein or devascularized kidney (G) [19]](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/361830789/figure/fig2/AS:1175395760111617@1657247595150/Classification-of-renal-trauma-using-the-American-Association-for-the-Surgery-of-Trauma.jpg)
A: grade 1, subcapsular hematoma/contusion, without laceration
B: grade 2, non-expanding peri-renal hematoma confined to perirenal fascia
C: grade 3
D: grade 4, parenchymal laceration extending through renal cortex, medulla
E: grade 4, laceration involving the collecting system with extravasation
F: grade 5, shattered kidney
G: grade 5, avulsion of renal hlum that devascularises kidney
처치
ABC 등의 외상 초기평가
혈역학적 안정, grade 1~3 injury → 절대 안정 및 비수술적 치료
grade 4 injury
안정적이고 수술 적응증이 없다면 절대안정 및 경과관찰 가능
불안정적이거나 수술적응증에 해당한다면 수술적 탐색 시행
** 비수술적 치료가 계획된 환자 중, 조영제 extravasation이 확인되거나, 신장주위 혈종의 직경(rim distance)이 25mm를 초과 또는 4cm 이상의 큰 혈종이 보이는 경우, 내측 혈종(medial hematoma)이 보이는 경우, 또는 적혈구 수혈을 2unit 이상 받은 환자는 혈관조영술 시행
혈액학적 불안정/grade 5 injury/수술의 적응증 → 수술적 탐색
수술 적응증
절대 적응증: 크기가 커지는 혈종, 박동성 혈종, 지속되는 신장 출혈
상대 적응증: 지속적인 urinary extravasation, nonviable renal parenchyma, 신동맥손상, 손상 정도가 파악되지 않은 경우, 다른 복부장기의 손상(colon,pancreas 등)
신장의 절반 이상이 보존될 수 있다면 재건이 가능한 상태로 보고 renorraphy 및 혈관과 collecting system의 봉합/문합을 시행
Hilum의 광범위한 손상이 있는 경우엔 수술적 재건이 불가
Devitalized renal parenchyma 부위가 크고, 소변 누출이 있다면 partial/total nephrectomy를 시행
[1] Sabiston, 21e. pg. 2078-2082
요관손상
진단 : 조영증강 CT
조영제의 extravasation
손상부위의 원위부에 조영제가 보이지 않음
손상부위의 수신증
(retrograde pyelography나 IVP는 급성기 손상에서 시행이 어려우며, 퀄리티가 낮아 선호되지 않음)
처치
traumatic ureteral laceration → 수술적 봉합 & ureteral stent 거치
traumatic ureteral contusion → 수술 (ureteral stent 또는 손상부위 절제 및 문합)
혈역학적으로 불안정 → temporary drainage 후 환자가 안정되면 근치수술을 계획
진단이 늦어지거나, 수술 후 경도의 손상이 발견되는 경우 → ureteral stenting
[1] Sabiston, 21e. pg. 2082-2083
방광손상
발생 기전
둔상이 가장 흔한 원인 (80%)
골반골절을 흔하게 동반 (80-95%)
임상양상
육안적 혈뇨 & 골반 골절
진단
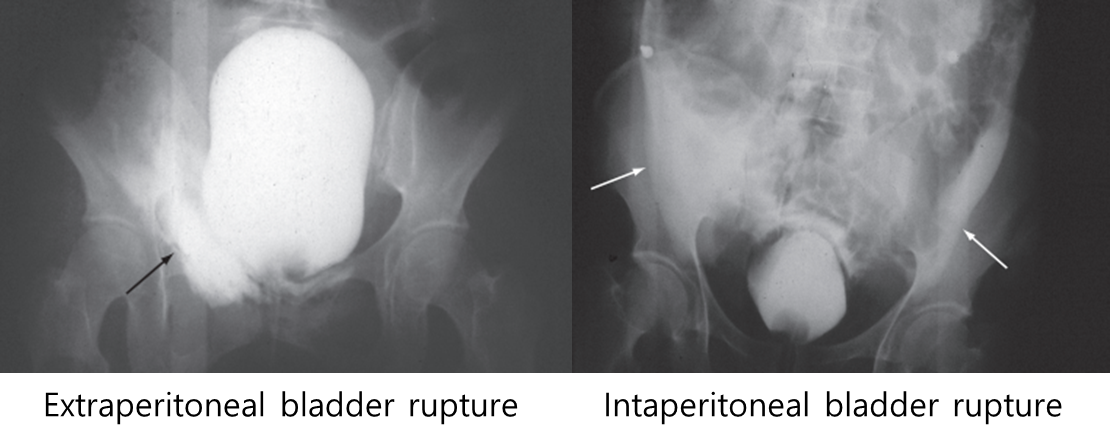
retrograde cystography (DOC)
plain cystography나 CT cystography를 사용해볼 수 있음
분류
Intraperitoneal rupture: bladder dome의 파열이 발생하면서 소변과 방광 내 주입한 조영제가 복강 내부로 유출되어 paracolic gutter 주변과 bowel loop 사이사이에서 조영제가 확인
Extraperitoneal rupture: 대부분 골반 골절과 동반되어 나타나며, 방광의 base 또는 anterolateral 부위가 파열되면서 복강 밖의 골반 내에 조영제가 유출
처치
Intraperitoneal rupture : 진단 즉시 수술적 치료
Extraperitoneal rupture : urinary catheter drain 및 경과관찰
** 관통성 방광 손상, 혈뇨가 지속되는 경우, 다른 골반 장기 손상이 동반된 경우, 방광 목(bladder neck) 손상, 방광 내 뼛조각이나 이물질이 들어간 경우 → 수술 필요
[1] Sabiston, 21e. pg. 2083-2084
요도손상
임상 양상
Classic triad : 요도구 출혈, 배뇨 불가, 급성 요폐색
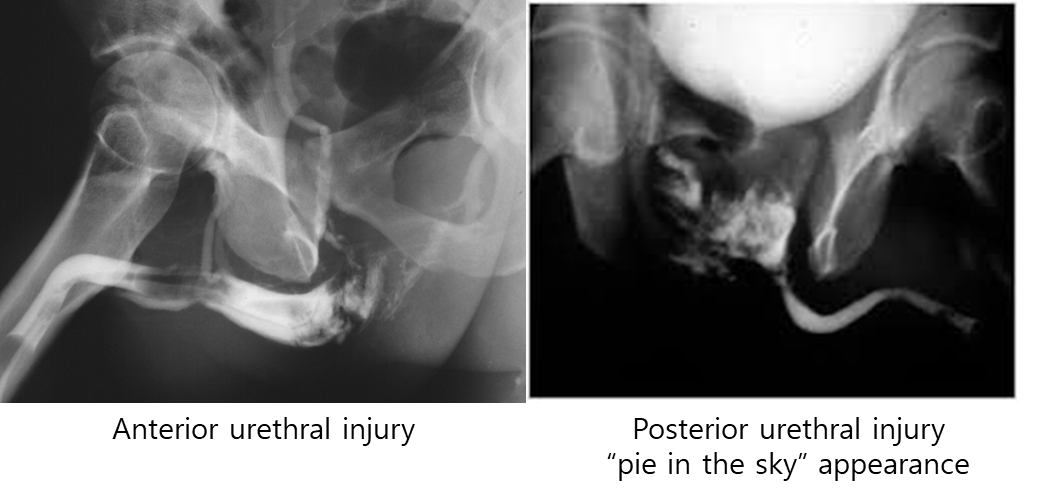
회음부 둔상은 anterior urethral injury, 골반 골절은 posterior urethral injury와 연관
하복부 통증
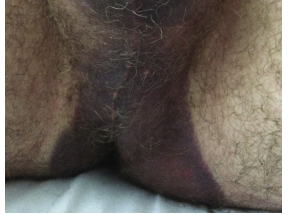
회음부 “butterfly” 혈종, 음낭 혈종 등
진단
요도 손상이 의심되는 환자라면 도뇨관 삽입 전 retrograde urethrography를 반드시 시행
** pie in the sky appearance: 후요도부위가 완전파열되고 큰 혈종이 발생하면서 방광이 위로 올라간 형태를 보임
처치
suprapubic cystostomy (두덩위 방광루) 우선 설치
posterior urethra의 완전 파열의 경우 cystostomy 후 3개월 뒤 수술적 치료 시행
[1] Sabiston, 21e. pg. 2084-2086
0개의 글
** 제목만 보더라도 어떤 내용인지 알 수 있도록 완성된 문장으로 작성해주세요.
예시) 초음파 (X) → 초음파 사진에서 PDA 소견을 어떻게 알 수 있나요? (O)